Console Guide (Old)
Threat Response Management Console Versions 3.x and 4.x¶
This chapter describes the options available to you in the Threat Response Appliance Management Console.
Note
For details on how to open this console, go to Opening Appliance Management Console..
The main area of the console page contains three tabs, each of which is associated with various subtabs. They are listed below and described in further detail in this chapter:
| Tab | Uses | Subtab |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Monitor the system | Summary, System Dump, CPU Load, Memory, Network, Storage Devices, File System, Login Attempts |
| Setup | Set up or modify the system configuration, Logging, Licenses, Upgrade, Reboot, among other things. | Interfaces, Routing, DNS, Hostname, Hosts, ARP, Web |
| View Logs | View current and archived logs. | Continuous Log, Current Log |
Monitoring tab overview¶
This section describes the administrative tasks associated with the Monitoring tab, including:
- Summary
- System Dump
- CPU Load
- Memory
- Network
- Storage Devices
- File System
- Login Attempts
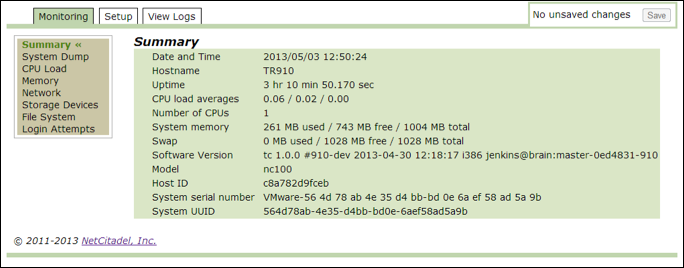
Summary¶
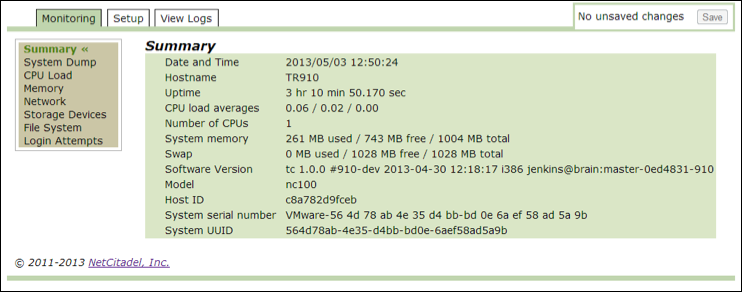
Use this option to review a summary of the key parameters for the Threat Response system. The CPU load averages are listed in increments of 1 minute, 5 minutes, and 15 minutes.
System dump¶
Use this option to troubleshoot your system with Threat Response technical support. Use the Generate button to create a UNIX TAR archive file, which includes log files. No passwords, security information, or other sensitive information is included in this file.
You can also use this window to include a fresh system configuration backup.
Note
You can make changes using this management console. But to commit them to the database, you must save the changes using the Save button on the top right-hand side of the page.
CPU load¶
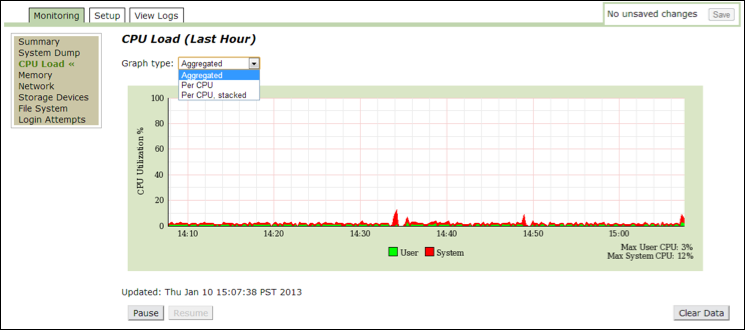
Use this option to view the details of CPU load in the past hour. This data is presented in graphical format and based on the following graphical options: Aggregated, Per CPU, or Per CPU Stacked. Use this data for troubleshooting to determine if the system is healthy.
Memory¶
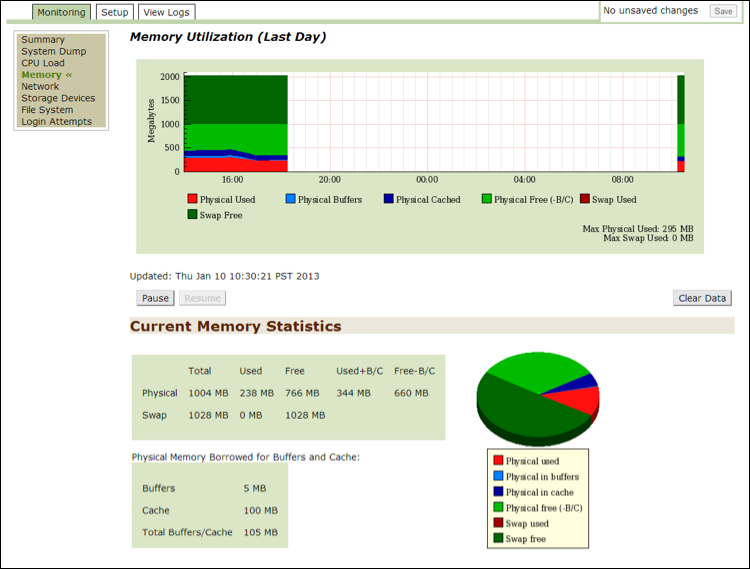
Use this option to view the details of memory usage in the past day in the form of a graph and pie chart. The graphical data is presented in megabytes and statistics relating to the pie chart are on the bottom of the page. Use this data for troubleshooting to determine if the system is healthy.
Network¶
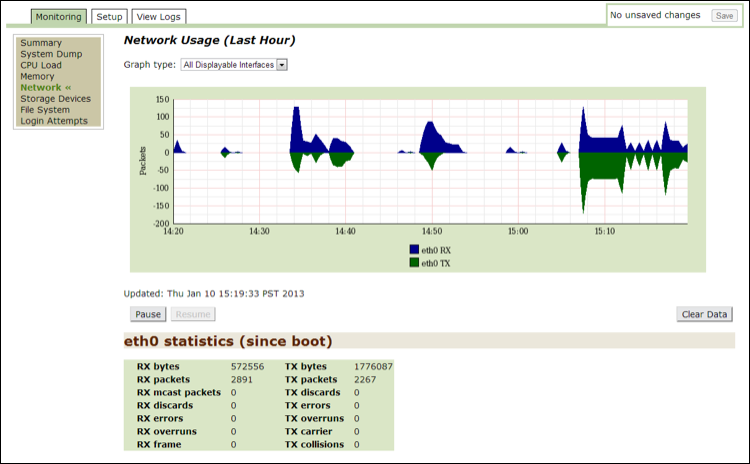
Use this option to view the details of network usage in the past hour. This data is presented in graphical format and based on the following graphical options: All Displayable Interfaces or Physical Interfaces. Statistics relating to the interface(s) are listed below the graph. Use this data for troubleshooting to determine if the system is healthy.
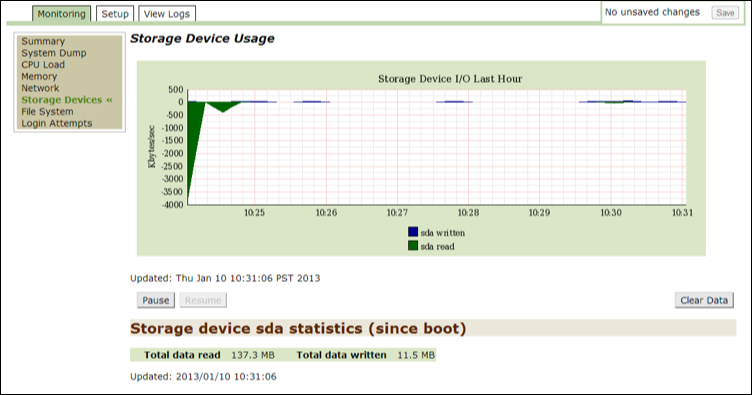
Storage devices¶
Use this option to determine how often the system reads and writes to a disk.
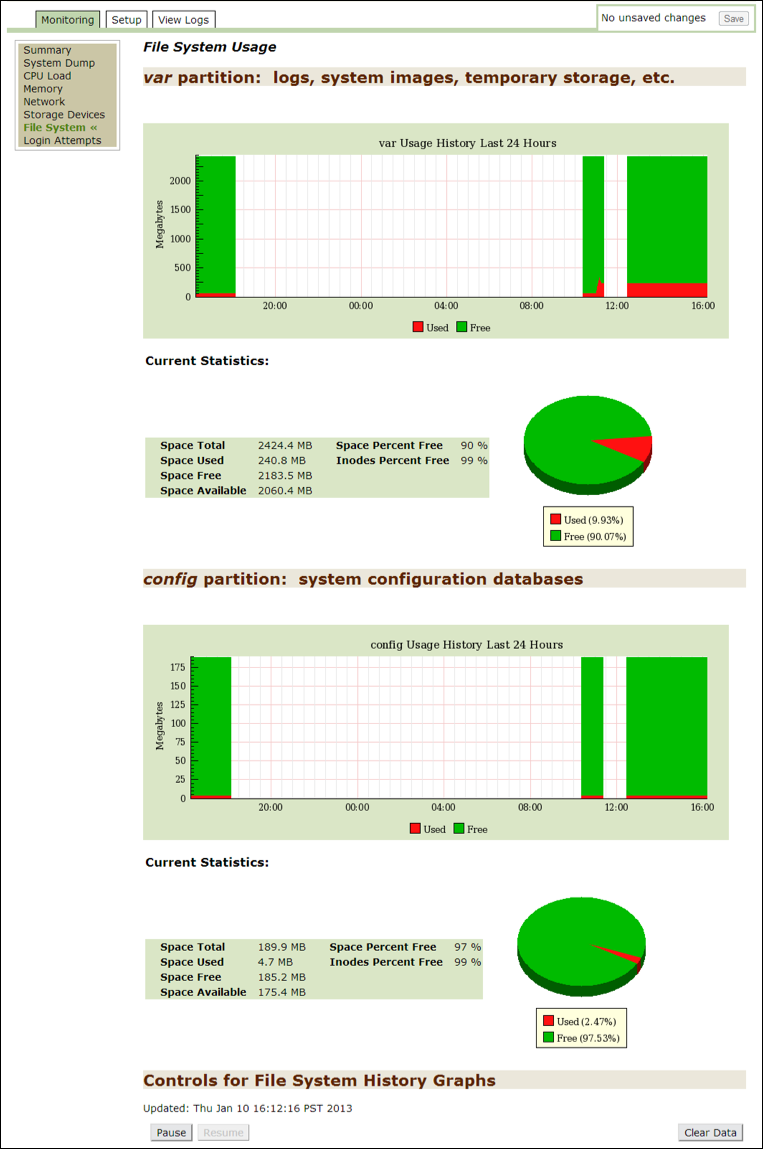
File system¶
Use this option to view the statistics for each partition. The var partition is used by Threat Response to store database files.
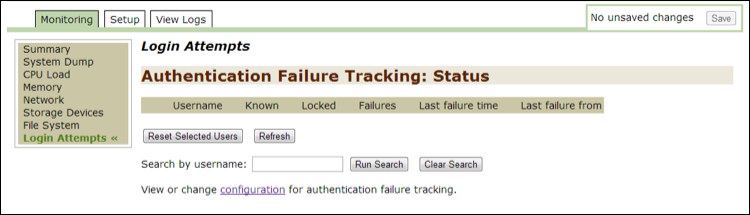
Login attempts¶
Use this option to track failed login attempts to the command line and to the Threat Response UI.
Threat Response:
- adds the data to the table.
- lists who attempted the login.
- lists when the attempted login occurred.
- lists the password used.
Use the search feature to search by users.
To reset one or more users, put a check mark next to your selection and then click on the Reset Selected Users button.
Click on the configuration link to open the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting page in the Setup tab.
Setup tab overview¶
This section describes the administrative tasks associated with the Setup tab, including:
- Interfaces
- Routing
- DNS
- Hostname
- Hosts
- ARP
- Web
- SSH
- AAA
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- LDAP
- SNMP
- Faults
- Logging
- Configurations
- Backups
- Data and Time
- NTP
- Licensing
- Certificates
- Reboot
- Upgrade
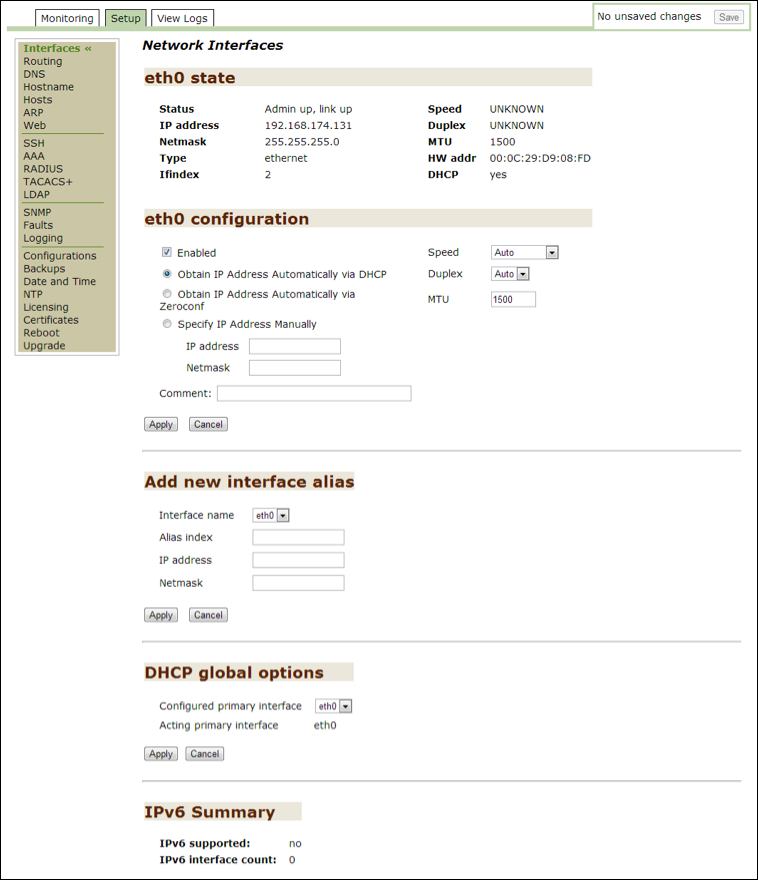
Interfaces¶
The Threat Response Installation Wizard lets you install one interface. Use this option to add multiple interfaces or modify existing interfaces.
Routing¶
Use this option to modify an IP routing configuration. You cannot remove the default eth0 route.
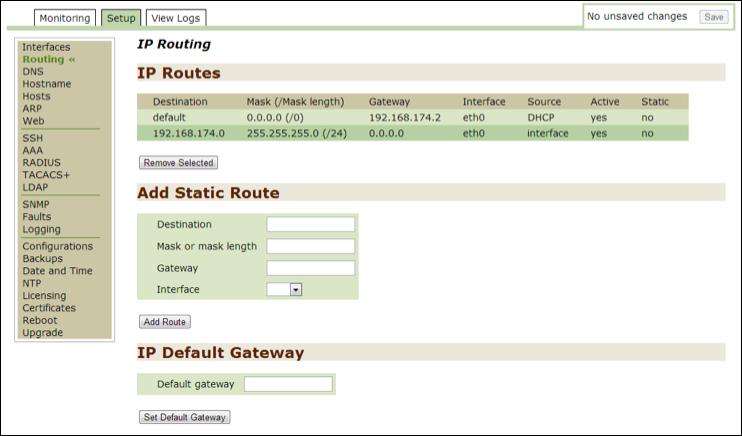
DNS¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current DNS settings.
Hostname¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current hostname information and banners. The name in the Host Name field is the same as the one you entered during the initial installation.
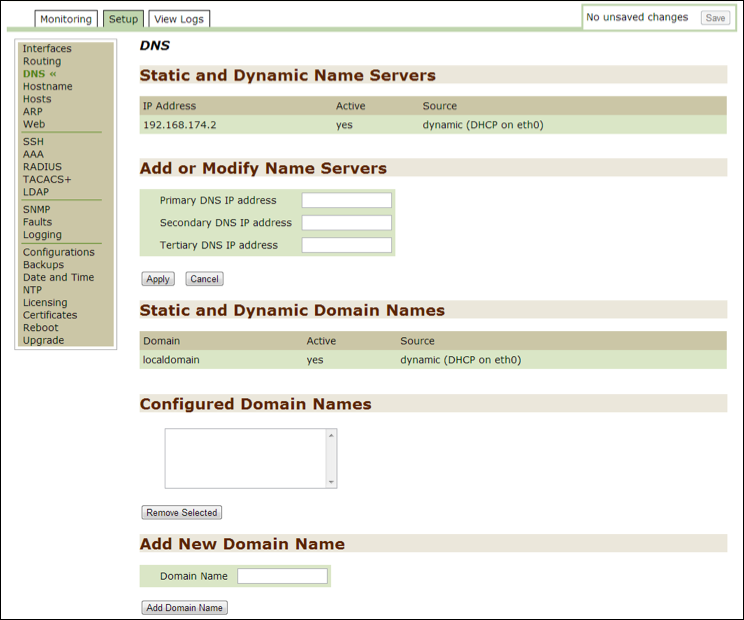
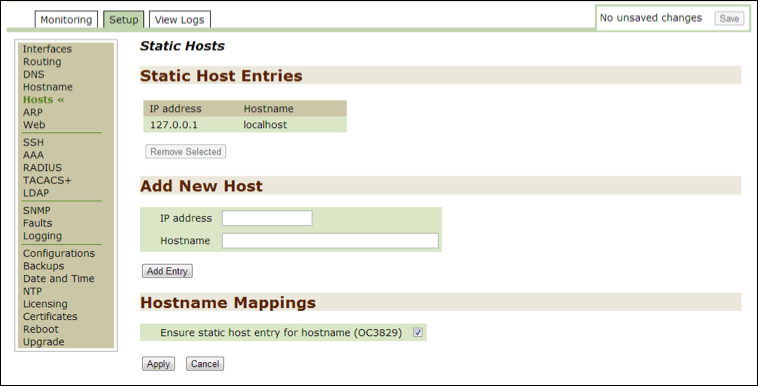
Hosts¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current host information. When the Hostname Mapping option is checked off, Threat Response ensures that the mapping entry for the host is in the file.
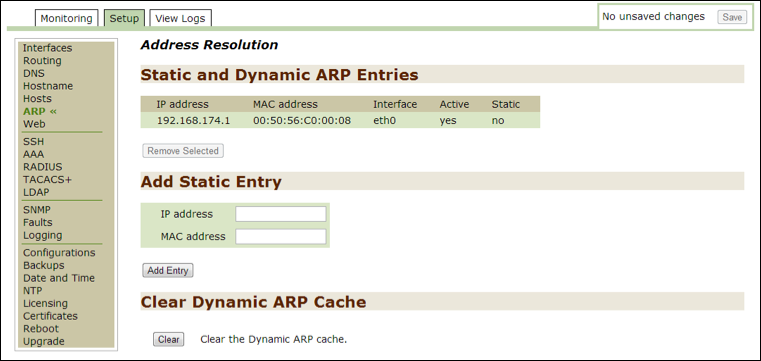
ARP¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current IP and MAC addresses. You cannot remove the default system address.
Web¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current Web settings for secure and non-secure Web sites. Use the HTTPS certificate name drop-down list to select any newly added certificates to the Installation Wizard.
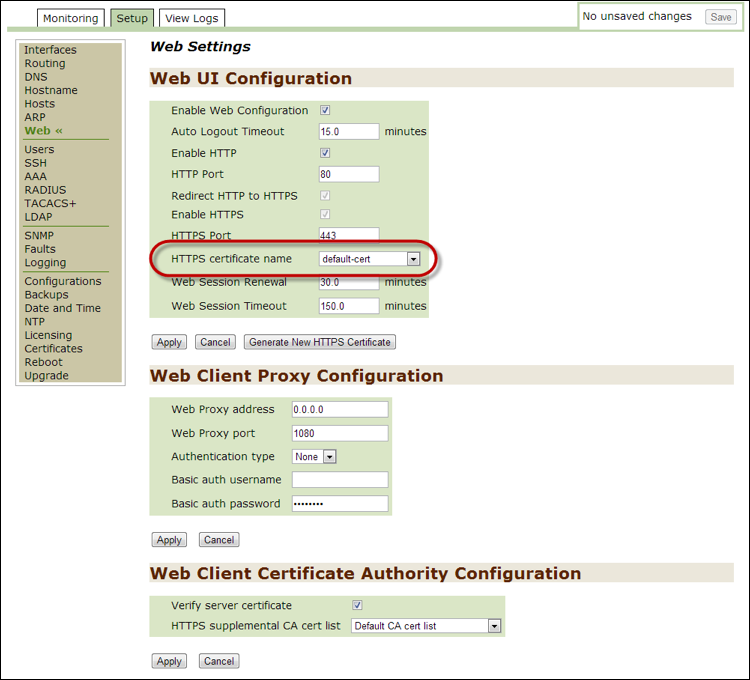
SSH¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current SSH settings and to access the CLI remotely. Newly generated host keys are added to the bottom of the list.
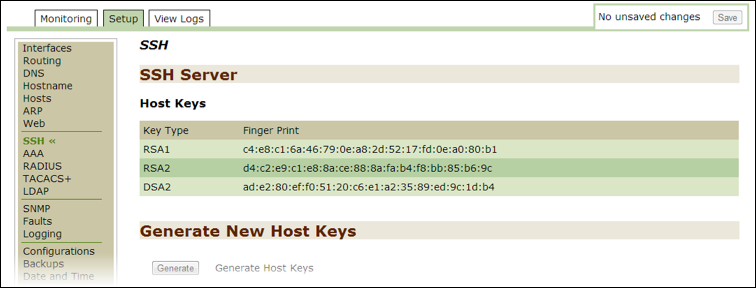
AAA¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current AAA settings. You can validate user authentication by setting up the following methods from the Authentication Method List in the Threat Response Appliance Management Console:
- Local
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- LDAP
Use the options in the Authentication Failure Tracking: Configuration section to modify how you track authentication failures.
Click on the status link to open the Login Attempts page in the Monitoring tab.
Note
Refer to the Setting user authentication. section in the second chapter of this guide for details on how to configure this option.
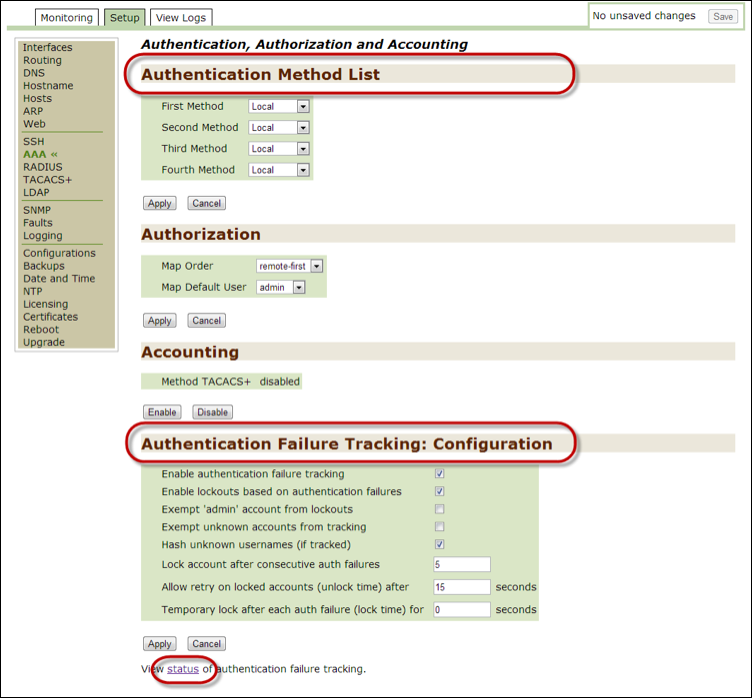
RADIUS¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current RADIUS settings, which are used to configure external authentication for systems using RADIUS.
TACACS+¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current TACACS+ settings.
LDAP¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current LDAP settings.
SNMP¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current SNMP settings, which are used to monitor statistics.
Faults¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current “fault” settings, which are used to report catastrophic errors. You can also use this option to set up email alerts.
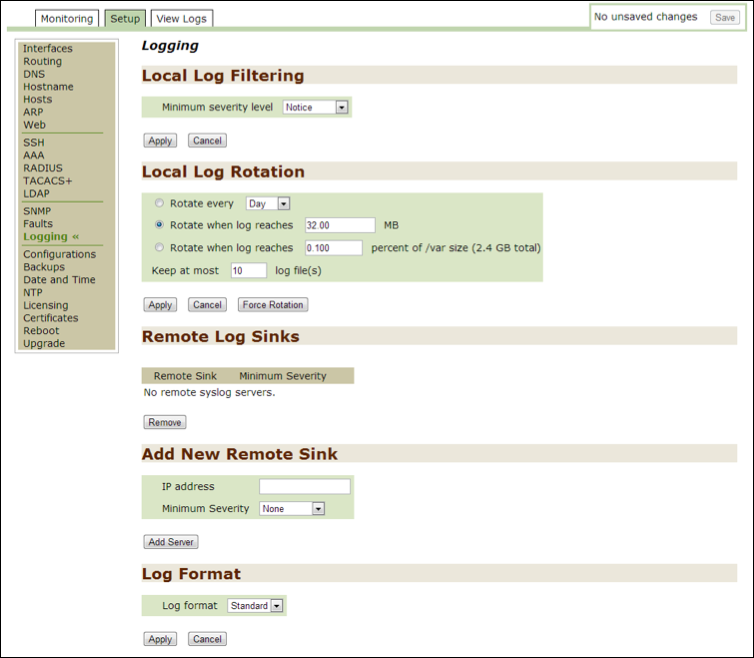
Logging¶
Use this option to monitor or modify current logging settings for the files seen in the View Logs tab as well as for those files used during a System Dump from the Monitoring tab.
Use the option in the Local Log Filtering section to select a minimum level of severity. Note that the higher levels of severity capture the most data. While this is useful for troubleshooting, be aware that the log files will grow much faster. The levels are listed below with the highest level of severity coming before all others:
- None
- Emergency
- Alert
- Critical
- Error
- Warning
- Info
- Debug
Use the options in the Local Log Rotation section to determine how often the files are to be archived.
Configurations¶
Use this option to modify current administrative settings, which are stored in the file system.
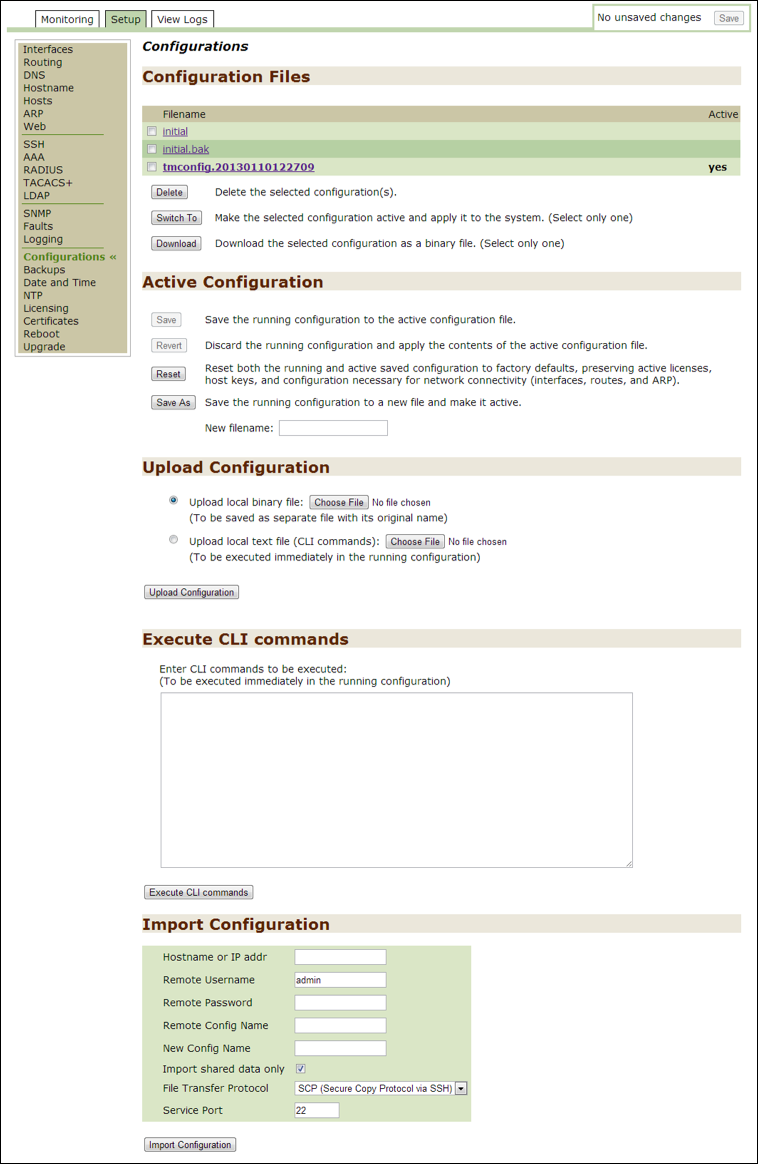
Active Configuration¶
Use the options in the Active Configuration section to:
Savethe running configuration to the active configuration file.- Revert (discard) the running configuration and apply the contents of the active configuration file.
- Reset both the running and active (saved) configurations to factory defaults, preserving active licenses, host keys, and configurations necessary for network connectivity (interfaces, routes, and ARP).
- Save the running configuration as a new file and activate it. Enter the new filename into the
New filenamefield.
Upload Configuration¶
Use one of the options in the Upload Configuration section to:
Upload a binary file: This option is available if you used the Download option above. Click on the Choose File button to locate a file. Note that this file is saved separately with its original name.Upload a local text file (CLI commands): Click on the Choose File button to locate a file. Note that this file is executed immediately in the running configuration.
Execute CLI Commands¶
Use the Execute CLI commands section to add CLI commands that can be executed immediately in the running configuration.
Import Configuration¶
Use the Import Configuration section to load administrative settings from another appliance.
Backups¶
Use this option to back up and restore system files.
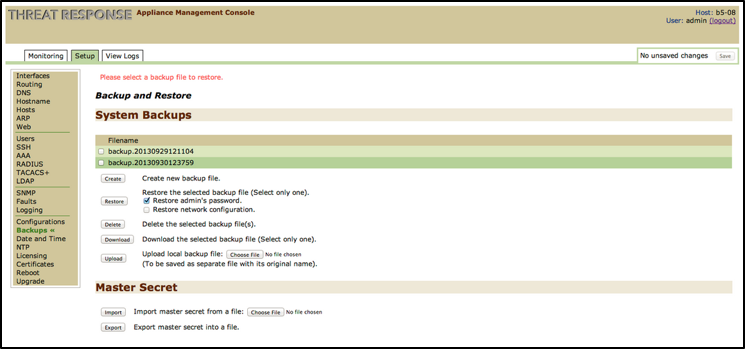
Create Backup File¶
Use the Create button to create a new backup file. This file includes the key to read encrypted passwords and other sensitive information.
Restore Backup File¶
Use the Restore button to restore one or more files to the system. Note that when you restore a backup file, you overwrite the current file containing any new configuration changes, including added data sources, devices, or users to Threat Response.
To complete the restoration process, select one or both of the following options: Restore admin’s password and/or Restore network configuration.
Delete Backup File¶
Use the Delete button to delete one or more files from the system.
Download Backup File¶
Use the Download button to download a file locally (one only).
Upload Backup File¶
Use the Upload button to upload a locally downloaded file. Click on the Choose File button to locate a file on your computer.
Import Master Secret File¶
Use the Import button to import the master secret file. Click on the Choose File button to locate the file on your computer.
Export Master Secret File¶
Use the Export button to export the master secret file.
Date and Time¶
Use this option to monitor and modify the Date and Time settings for Threat Response. Changes to this page do not need to be saved once you have clicked on the Apply button.
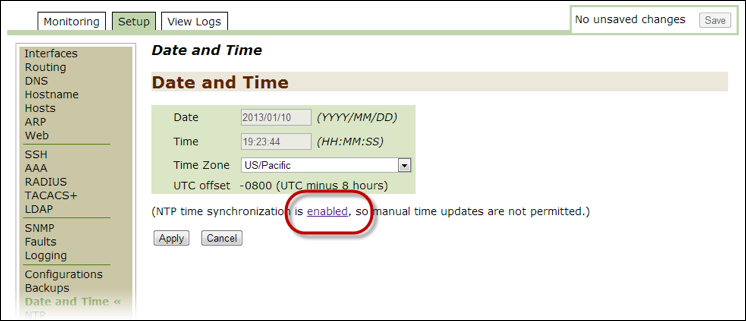
Note
If the NTP time synchronization option is enabled, you cannot change these values manually. To disable NTP, click on the enabled link and follow the instructions in the NTP configuration of second chapter of this guide.
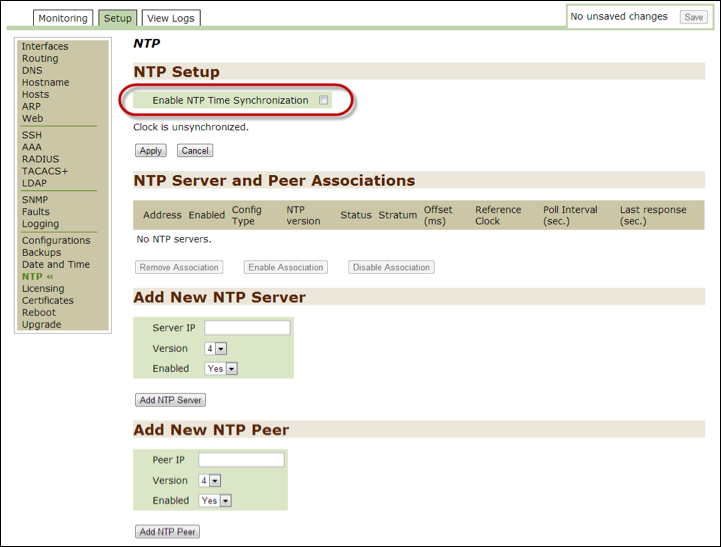
NTP¶
Use this option to monitor and modify the NTP settings to enable or disable the Network Time Protocol for Threat Response. For details on how to use the options in this section, follow the instructions in the NTP configuration of second chapter of this guide.
Note
Some data sources are not accessible if the host clock does not reflect the correct local time.
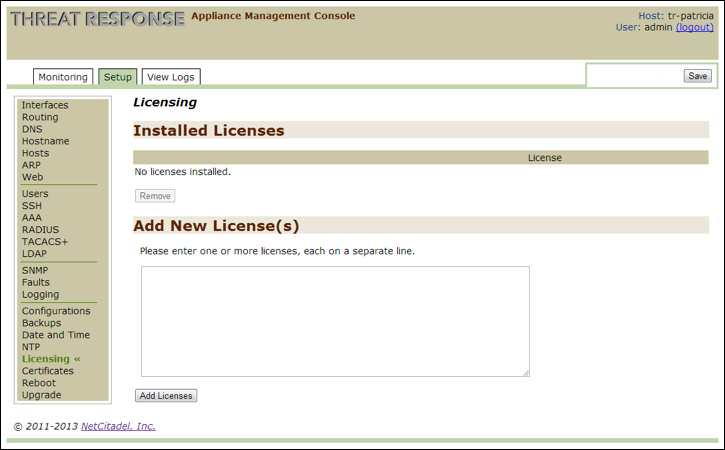
Licensing¶
Use this option to add or remove one or more licenses.
Certificates¶
Use this option to monitor and modify the Certificate settings for secure and non-secure Web addresses. Threat Response uses self-signed certificates by default. If you use an outside authority, enter the certificate string, as well as the key string, into this section.
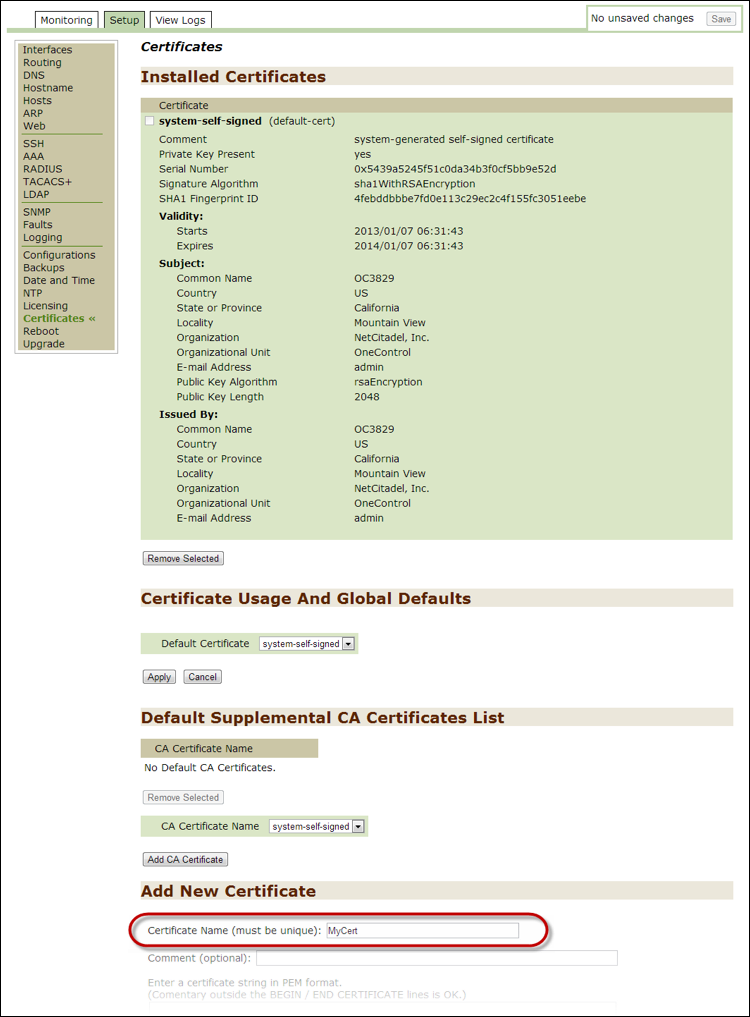
It can be selected from the HTTPS certificate name drop-down list on the Web page.
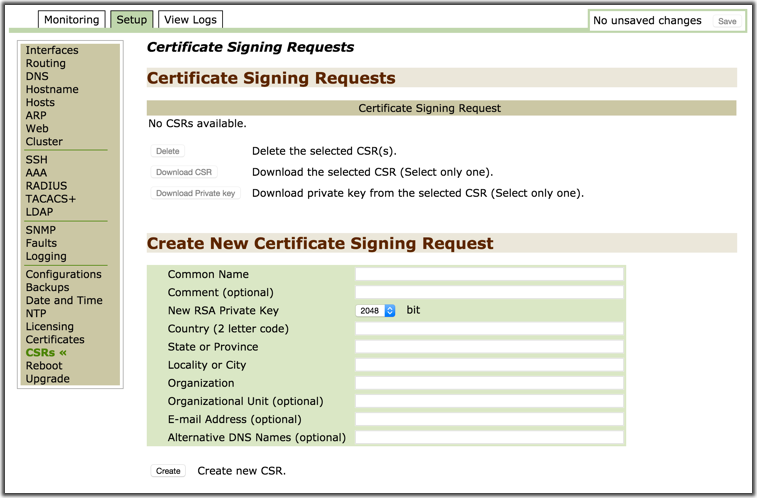
CSRs¶
Use this option to create Certificate Signing Requests (CSRs) in Threat Response. A CSR can then be uploaded to a certificate server or Certificate Authority (CA) to generate a signed certificate for use in Threat Response.
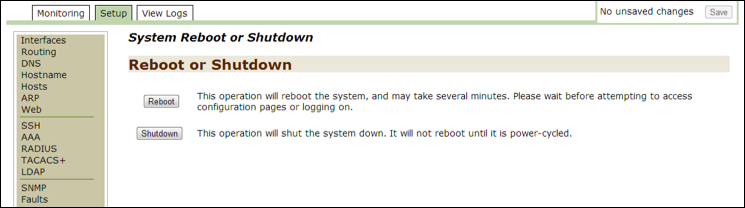
Reboot¶
Use this option to monitor and modify Reboot settings. After you reboot, save any unsaved changes.
Note
For details on how to use the options in this section, follow the instructions in the Initiate Reboot section of second chapter of this guide.
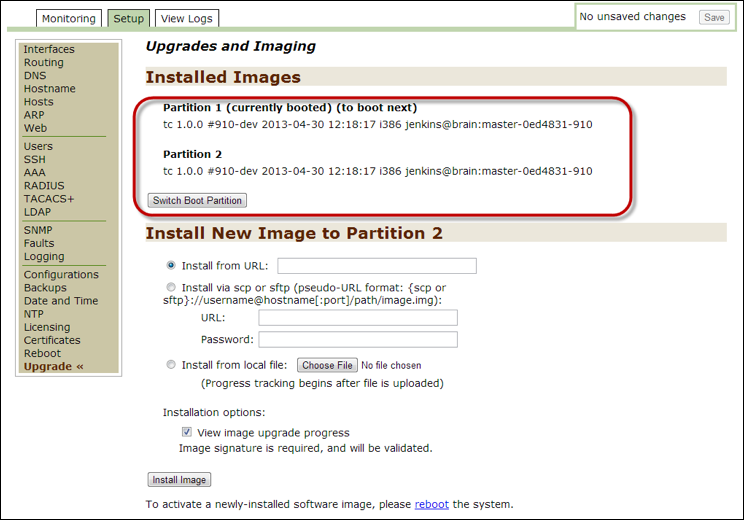
Upgrade¶
Use this option to monitor and modify Upgrade settings. Threat Response always installs two partitions with two versions of the system. This is especially useful when you install an upgrade or patch. Use the Switch Boot Partition button to switch between these two images, if necessary. If you use this option, reboot the system in order to use the switched version.
Note
On how to install a new image, follow the instructions in the “Upgrade” section in the second chapter of this guide: “Using the Threat Response Appliance Management Console.”
View Logs¶
This section describes the administrative tasks associated with the View Logs tab, including:
- Continuous Log
- Current Log
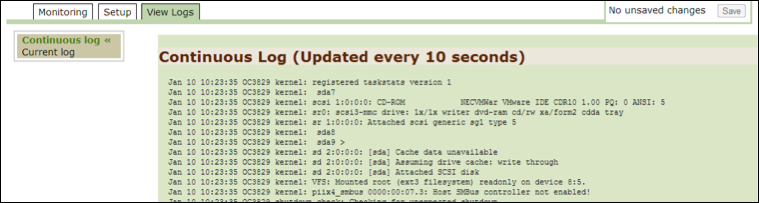
Continuous Log¶
Use this option to monitor continuous logs. These logs are the default system logs that change in real time. Use them for troubleshooting.
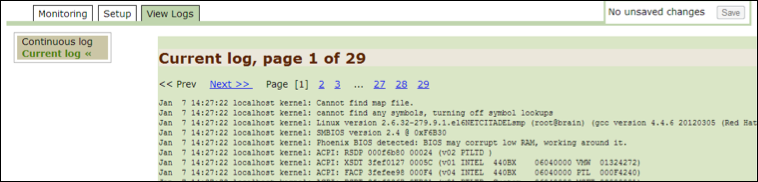
Current Log¶
Use this option to monitor archived logs.
Opening Appliance Management Console¶
Use the steps in this section to open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console:
- Open a browser window and enter:
https://<Threat Response-ipaddress>:8080. - Provide the Proofpoint
usernameandpasswordand then pressEnterto open the Proofpoint Appliance Management Console window. - Click on Login to open the Summary page.
NTP configuration¶
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) automatically synchronizes the time set for Threat Response. If the time is not set correctly, then you may not be able to connect to some data sources.
If you want to modify the date and time after specifying an NTP server during installation, you must first disable the NTP option in the Threat Response Appliance Management Console to manually set the date, time, and time zone in the Date and Time subtab.
To disable NTP time synchronization:
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
NTPon the left-hand panel to open the NTP window. - Go to the
NTP Setupsection at the top of the page. - Deselect the
Enable NTP Time Synchronizationcheckbox. - Click on
Applyand then click onSavein the upper right-hand corner of the window to save the change.
Date and Time configuration¶
The date and time can affect data source connectivity. If it is configured incorrectly, you may not be able to connect to some data sources.
To set up the date and time for Threat Response with the correct local time:
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Date and Timeon the left-hand panel to open the window where you can configure the date, time, and time zone options. Note: If the NTP time synchronization option is enabled, then you cannot change these values manually. To disable NTP, click on the enabled link and then follow the instructions in the aforementioned section. - Enter the local date, time, and time zone in the
Date and Timesection.- The Date format is
YYYY/MM/DD. - The Time format is
HH:MM:SS.
- The Date format is
- Click on Apply and then click on Save in the upper right-hand corner of the window to save the changes.
License keys¶
Threat Response uses yearlong subscription-based licensing for product delivery.
Note
It is important to update the OneControl configuration with the new license before the subscription expires.
This section describes how to add or remove an existing OneControl license.
Adding OneControl license¶
- Go to the Proofpoint License Update email containing your new or updated license key.
- Select and copy the license key number.
- Open the Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Licensingon the left-hand panel to open theLicensingpage. - Paste the license from the Proofpoint License Update email into the text box under
Add New License(s).- If you have multiple licenses to add, use a separate line for each one.
- Click on
Add Licensesand then click onSavein the upper right-hand corner of the window to save the changes.- Any new licenses are added to the Installed Licenses section with status information..
Removing OneControl license¶
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Licensingon the left-hand panel to open theLicensingpage. - Put a check mark by the current license, click on
Remove, and then click onSavein the upper right-hand corner of the window to save the change.
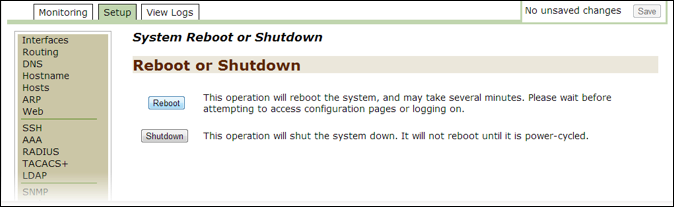
Initiate reboot¶
A system reboot may take several minutes. Please wait before you attempt to access the configuration pages or before you log on.
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Rebooton the left-hand panel to open theSystem Reboot or Shutdownpage. - Click on the
Rebootbutton to reboot the system.- This operation logs you out of the system while it is rebooting.
- Wait a few minutes and then click on the
click herelink to return to the Threat Response Appliance Management Console Login window.

- Log in with your
usernameandpasswordand then click onLogin.
Upgrade Threat Response¶
This section describes how to upgrade an image, such as patches.
- Open the release notes for the new image.
- Follow the instructions for downloading the latest image to your hard drive and then note the download destination.
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Upgradeon the left-hand panel to open theUpgrades and Imagingpage.
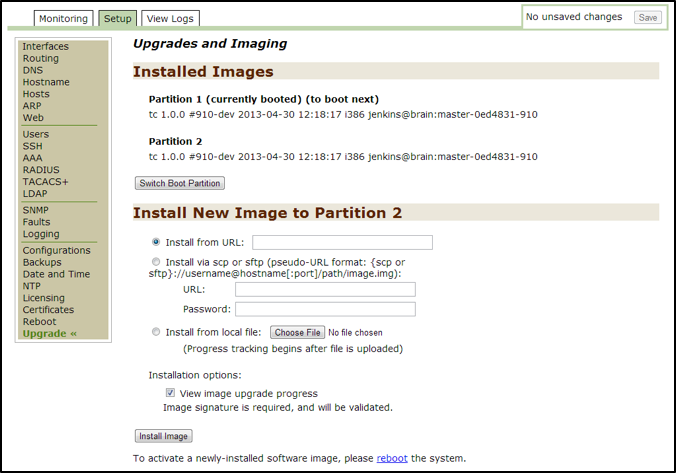
- In the
Install New Image to Partitionsection, selectInstall from the local fileand then click onChoose File. - Browse to the location of the downloaded image (from “Step 2” of this section).
- Select the file and then click on
Open. - Optional: Click on the installation option (View image upgrade progress) to view the details and status of the installation progress in real time.
- Click on
Install Image. (If necessary, scroll down to see this button.)- After the file is uploaded, the Image Upgrade Status window lets you track the upgrade progress if you put a check mark by the View image upgrade progress option above.
- When the upgrade is complete, click on
OKin theImage Upgrade Statuswindow to return to theUpgrades and Imagingwindow. - Scroll to the bottom of the page and then click on the
rebootlink, which opens the System Reboot or Shutdown window. - Click on the
Rebootbutton to open the System Reboot or Shutdown page.- This operation logs you out of the system while it is rebooting.
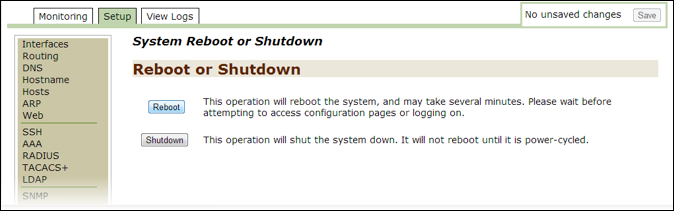
- Wait a few minutes and then click on the
click herelink to return to the Threat Response Appliance Management Console Login window.

- Log in with your
usernameandpasswordand then click onLogin.
Data backup¶
This section describes how to back up your system files.
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Backupson the left-hand panel to create backup files. - Click on the
Createbutton to create a new backup file.- Threat Response automatically creates the file, names it
backup.<datetimestamp>and then adds the file to the bottom of the Filename list with a summary of the operation at the top of the page.
- Threat Response automatically creates the file, names it
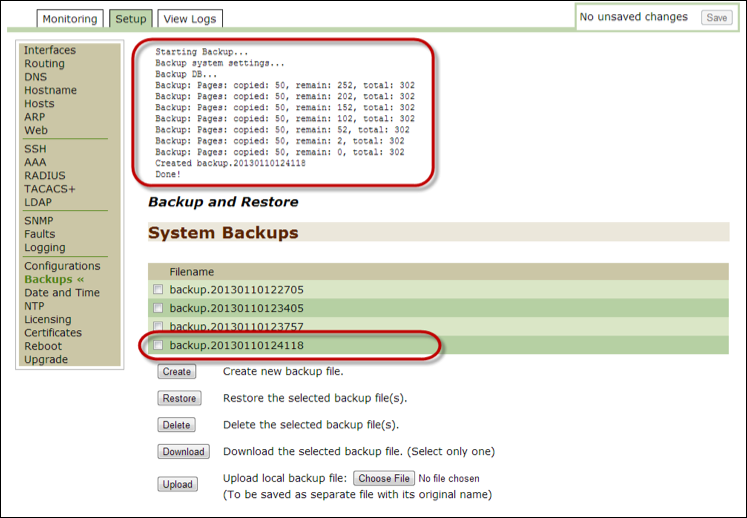
Alongside each backup file, there is a checkbox so as to enable you to restore, delete, or download a file.
Restore data¶
This section describes how to restore previously backed up files.
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and then click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
Backupson the left-hand panel to restore backed up files. - Select a backed-up file from the Filename list.
- Click on the
Restorebutton.
Setting User Authentication¶
Users with administrative privileges can add and modify user accounts, as well as authenticate users in the Threat Response UI. The settings can be configured in the Threat Response Appliance Management Console.
This section describes the user authentication process:
- Open the Threat Response Appliance Management Console and click on the
Setuptab. - Click on
AAAto open the Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting page. - Go to the
Authentication Method Listsection.- Authentication takes place via the following choices and in the order in which you designate them.
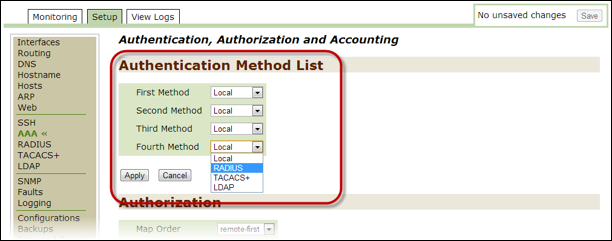
- Go to the
First Methodfield and then select a type of method. The options follow:- Local (default)
- RADIUS
- TACACS+
- LDAP
- Repeat “Step 4” of this section for the
Second Methodthrough theFourth Method. - Click on
Applyand then go to the top of the page and click onSave. - Depending on your selections in the previous two steps, go to the Setup pages to make the appropriate changes.
- For instance, if you selected
LDAP, go to theSetup > LDAPpage to configure the global LDAP settings and servers or add a new LDAP server.
- For instance, if you selected
- Click on
Saveat the top of the page to save all changes.